The history of Indonesia has been shaped by its geographic position, its natural resources, a series of human migrations and contacts, wars and conquests, as well as by trade, economics and politics. Indonesia is an archipelagic country of 17,508 islands (6,000 inhabited) stretching along the equator in South East Asia. The country's strategic sea-lane position fostered inter-island and international trade; trade has since fundamentally shaped Indonesian history. The area of Indonesia is populated by peoples of various migrations, creating a diversity of cultures, ethnicities, and languages. The archipelago's landforms and climate significantly influenced agriculture and trade, and the formation of states. The boundaries of the state of Indonesia represent the twentieth century borders of the Dutch East Indies.

Fossilised remains of Homo erectus and his tools, popularly known as the "Java Man", suggest the Indonesian archipelago was inhabited by at least 1.5 million years ago.Austronesian people, who form the majority of the modern population, are thought to have originally been from Taiwan and arrived in Indonesia around 2000 BCE. From the 7th century CE, the powerful Srivijaya naval kingdom flourished bringing Hindu and Buddhistinfluences with it. The agricultural Buddhist Sailendra and Hindu Mataram dynasties subsequently thrived and declined in inland Java. The last significant non-Muslim kingdom, the Hindu Majapahit kingdom, flourished from the late 13th century, and its influence stretched over much of Indonesia. The earliest evidence of Islamised populations in Indonesia dates to the 13th century in northern Sumatra; other Indonesian areas gradually adopted Islam which became the dominant religion in Java and Sumatra by the end of the 16th century. For the most part, Islam overlaid and mixed with existing cultural and religious influences.
Europeans arrived in Indonesia from the 16th century seeking to monopolise the sources of valuable nutmeg, cloves, and cubeb pepper in Maluku. In 1602 the Dutch established the Dutch East India Company (VOC) and became the dominant European power by 1610. Following bankruptcy, the VOC was formally dissolved in 1800, and the government of the Netherlands established the Dutch East Indies under government control. By the early 20th century, Dutch dominance extended to the current boundaries. The Japanese invasion and subsequent occupation in 1942-45 during WWII ended Dutch rule, and encouraged the previously suppressed Indonesian independence movement. Two days after the surrender of Japan in August 1945, nationalist leader, Sukarno, declared independence and became president. The Netherlands tried to reestablish its rule, but a bitter armed and diplomatic struggle ended in December 1949, when in the face of international pressure, the Dutch formally recognised Indonesian independence.
An attempted coup in 1965 led to a violent army-led anti-communist purge in which over half a million people were killed. General Suharto politically outmanoeuvred President Sukarno, and became president in March 1968. His New Order administration garnered the favour of the West whose investment in Indonesia was a major factor in the subsequent three decades of substantial economic growth. In the late 1990s, however, Indonesia was the country hardest hit by the East Asian Financial Crisis which led topopular protests and Suharto's resignation on 21 May 1998. The Reformasi era following Suharto's resignation, has led to a strengthening of democratic processes, including a regional autonomy program, the secession of East Timor, and the first direct presidential election in 2004. Political and economic instability, social unrest, corruption, natural disasters, and terrorism have slowed progress. Although relations among different religious and ethnic groups are largely harmonious, acute sectarian discontent and violence remain problems in some areas.
Prehistory
In 2007 analysis of cut marks on two bovid bones found in Sangiran, showed them to have been made 1.5 to 1.6 million years ago by clamshell tools. This is the oldest evidence for the presence of early man in Indonesia. Fossilised remains of Homo erectus, popularly known as the "Java Man" were first discovered by the Dutch anatomist Eugène Dubois at Trinil in 1891, and are at least 700,000 years old, at that time the oldest human ancestor ever found. Further Homo erectus fossils of a similar age were found at Sangiran in the 1930`s by the anthropologist Gustav Heinrich Ralph von Koenigswald, who in the same time period also uncovered fossils at Ngandong alongside more advanced tools, re-dated in 2011 to between 550,000 and 143,000 years old. In 1977 anotherHomo erectus skull was discovered at Sambungmacan[3]
In 2003, on the island of Flores, fossils of a new small hominid dated between 74,000 and 13,000 years old and named "Flores Man" (Homo floresiensis) were discovered much to the surprise of the scientific community. This 3 foot tall hominid is thought to be a species descended from Homo Erectus and reduced in size over thousands of years by a well known process called island dwarfism. Flores Man seems to have shared the island with modern Homo sapiens until only 12,000 years ago, when they became extinct. In 2010 stone tools were discovered on Flores dating from 1 million years ago, which is the oldest evidence anywhere in the world that early man had the technology to make sea crossings at this very early time.
The archipelago was formed during the thaw after the latest ice age. Early humans to travelled by sea and spread from mainland Asiaeastward to New Guinea and Australia. Homo sapiens reached the region by around 45,000 years ago. In 2011 evidence was uncovered in neighbouring East Timor, showing that 42,000 years ago these early settlers had high-level maritime skills, and by implication the technology needed to make ocean crossings to reach Australia and other islands, as they were catching and consuming large numbers of big deep sea fish such as tuna.
Austronesian people form the majority of the modern population. They may have arrived in Indonesia around 2000 BCE and are thought to have originated in Taiwan. Dong Son culture spread to Indonesia bringing with it techniques of wet-field rice cultivation, ritual buffalo sacrifice, bronze casting, megalithic practises, and ikat weaving methods. Some of these practices remain in areas including the Batak areas of Sumatra, Toraja in Sulawesi, and several islands in Nusa Tenggara. Early Indonesians were animists who honoured the spirits of the dead as their souls or life force could still help the living.
Ideal agricultural conditions, and the mastering of wet-field rice cultivation as early as the 8th century BCE,allowed villages, towns, and small kingdoms to flourish by the 1st century CE. These kingdoms (little more than collections of villages subservient to petty chieftains) evolved with their own ethnic and tribal religions. Java's hot and even temperature, abundant rain and volcanic soil, was perfect for wet rice cultivation. Such agriculture required a well organized society in contrast to dry-field rice which is a much simpler form of cultivation that doesn't require an elaborate social structure to support it.
Buni culture clay pottery was flourished in coastal northern West Java and Banten around 400 BCE to 100 CE The Buni culture was probably the predecessor of Tarumanagara kingdom, one of the earliest Hindu kingdom in Indonesia that produces numerous inscriptions, which marked the beginning of historical period in Java.
Early kingdoms
References to the Dvipantara or Yawadvipa, a Hindu kingdom in Java and Sumatra appear in Sanskrit writings from 200 BCE. In India's earliest epic, the Ramayana, Sugriva, the chief of Rama's army dispatched his men to Yawadvipa, the island of Java, in search of Sita.The earliest archeological relic discovered in Indonesia is from the Ujung Kulon National Park, West Java, where an early Hindu statue of Ganesha estimated from the 1st century CE was found on the summit of Mount Raksa in Panaitan island. There is also archeological evidence of Sunda kingdom in West Java dating from the 2nd-century, and Jiwa Temple in Batujaya, Karawang, West Java was probably built around this time. South Indian culture was spread to Southeast Asia by the south IndianPallava dynasty in the 4th and 5th century. and by 5th century, stone inscriptions written in Pallava scripts were found in Java and Borneo.


One such early kingdom was Tarumanagara, which flourished between 358 and 669 CE. Located in West Java close to modern-day Jakarta, its 5th century king, Purnawarman, established the earliest known inscriptions in Java, the Ciaruteun inscription located near Bogor. On this monument, King Purnavarman inscribed his name and made an imprint of his footprints, as well as his elephant's footprints. The accompanying inscription reads, "Here are the footprints of King Purnavarman, the heroic conqueror of the world". This inscription is written in Pallava script and inSanskrit and is still clear after 1500 years. Purnawarman apparently built a canal that changed the course of the Cakung River, and drained a coastal area for agriculture and settlement purpose. In his stone inscriptions, Purnawarman associated himself with Vishnu, and Brahmins ritually secured the hydraulic project.
Three rough plinths dating from the beginning of the 4th century are found in Kutai, East Kalimantan, near Mahakam River. The plinths bear an inscription in the Pallava script of India reading "A gift to the Brahmin priests".
The political history of Indonesian archipelago during the 7th to 11th centuries was dominated by Srivijaya based in Sumatra, alsoSailendra that dominated central Java and constructed Borobudur, the largest Buddhist monument in the world. The history prior of of the 14th and 15th centuries is not well known due to scarcity of evidence. Two major states dominated this period; Majapahit in East Java, the greatest of the pre-Islamic Indonesian states, and Malacca on the west coast of the Malay Peninsula, arguably the greatest of the Muslim trading empires.
Medang or previously known as Mataram was an Indianized kingdom based in Central Java around modern-day Yogyakarta between the 8th and 10th centuries. The center of the kingdom was moved from central Java to east Java by Mpu Sindok. An eruption of Mount Merapi volcano or a power struggle may have caused the move.
The first king of Mataram was Sri Sanjaya and left inscriptions in stone.[15] The monumental Hindu temple of Prambanan in the vicinity of Yogyakarta was built by Daksa. Dharmawangsa ordered the translation of the Mahabharata into Old Javanese in 996.
The kingdom collapsed into chaos at the end of Dharmawangsa's reign under military pressure fromSrivijaya. One of the last major kings of Mataram was Airlangga who reigned from 1016 until 1049.Airlangga was a son of Udayana of Bali and a relative of Dharmawangsa re-established the kingdom including Bali under the name of Kahuripan.

Prambanan in Java; built during the Sanjaya dynasty of Mataram, it is one of the largest Hindu temple complexes in south-east Asia.
Srivijaya was an ethnic Malay kingdom on Sumatra which influenced much of the Maritime Southeast Asia. From the 7th century CE, the powerful Srivijaya naval kingdom flourished as a result of trade and the influences of Hinduism and Buddhism that were imported with it.
Srivijaya was centred in the coastal trading centre of present day Palembang. Srivijaya was not a "state" in the modern sense with defined boundaries and a centralized government to which the citizens own allegiance. Rather Srivijaya was a confederacy form of society centered on a royal heartland. It was athalassocracy and did not extend its influence far beyond the coastal areas of the islands of Southeast Asia. Trade was the driving force of Srivijaya just as it is for most societies throughout history.[20] The Srivijayan navy controlled the trade that made its way through the Strait of Malacca.
By the 7th century, the harbors of various vassal states of Srivijaya lined both coasts of the Straits of Melaka. Around this time, Srivijaya had established suzerainty over large areas of Sumatra, western Java, and much of the Malay Peninsula. Dominating the Malacca and Sunda straits, the empire controlled both the Spice Route traffic and local trade. It remained a formidable sea power until the 13th century. This spread the ethnic Malay culture throughout Sumatra, the Malay Peninsula, and western Borneo. A stronghold ofVajrayana Buddhism, Srivijaya attracted pilgrims and scholars from other parts of Asia.
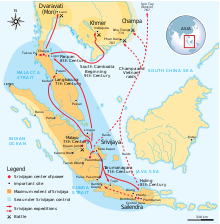
The relation between Srivijaya and the Chola Empire of south India was friendly during the reign of Raja Raja Chola I but during the reign of Rajendra Chola I the Chola Empire attacked Srivijaya cities. A series of Chola raids in the 11th century weakened the Srivijayan hegemony and enabled the formation of regional kingdoms based, like Kediri, on intensive agriculture rather than coastal and long distance trade. Srivijayan influence waned by the 11th century. The island was in frequent conflict with the Javanese kingdoms, first Singhasari and then Majapahit. Islam eventually made its way to the Aceh region of Sumatra, spreading its influence through contacts with Arabs and Indian traders. By the late 13th century, the kingdom of Pasai in northern Sumatra converted to Islam. The last inscription dates to 1374, where a crown prince, Ananggavarman, is mentioned. Srivijaya ceased to exist by 1414, when Parameswara, the kingdom's last prince, converted to Islam and founded the Sultanate of Malacca on the Malay peninsula.
Despite a lack of historical evidence, it is known that Majapahit was the most dominant of Indonesia's pre-Islamic states. The Hindu Majapahit kingdom was founded in eastern Java in the late 13th century, and under Gajah Mada it experienced what is often referred to as a "Golden Age" in Indonesian history, when its influence extended to much of southern Malay Peninsula, Borneo, Sumatra, and Bali[citation needed] from about 1293 to around 1500.
The founder of the Majapahit Empire, Kertarajasa, was the son-in-law of the ruler of the Singhasarikingdom, also based in Java. After Singhasari drove Srivijaya out of Java in 1290, the rising power of Singhasari came to the attention of Kublai Khan in China and he sent emissaries demanding tribute. Kertanagara, ruler of the Singhasari kingdom, refused to pay tribute and the Khan sent apunitive expedition which arrived off the coast of Java in 1293. By that time, a rebel from Kediri, Jayakatwang, had killed Kertanagara. The Majapahit founder allied himself with the Mongols against Jayakatwang and, once the Singhasari kingdom was destroyed, turned and forced his Mongol allies to withdraw in confusion.

Wringin Lawang, the split gate shows the red brick construction, and strong geometric lines of Majapahit architecture. Located at Jatipasar, Trowulan, East Java.
Gajah Mada, an ambitious Majapahit prime minister and regent from 1331 to 1364, extended the empire's rule to the surrounding islands. A few years after Gajah Mada's death, the Majapahit navy captured Palembang, putting an end to the Srivijayan kingdom. Although the Majapahit rulers extended their power over other islands and destroyed neighbouring kingdoms, their focus seems to have been on controlling and gaining a larger share of the commercial trade that passed through the archipelago. About the time Majapahit was founded, Muslim traders and proselytisers began entering the area. After its peak in the 14th century, Majapahit power began to decline and was unable to control the rising power of the Sultanate of Malacca. Dates for the end of the Majapahit Empire range from 1478 to 1520. A large number of courtiers, artisans, priests, and members of the royal family moved east to the island of Bali at the end of Majapahit power.
The age of Islamic states
The earliest accounts of the Indonesian archipelago date from the Abbasid Caliphate, according to those early accounts the Indonesian archipelago were famous among early muslim sailors mainly due to its abundance of precious spice trade commodities such as nutmeg, cloves, galangal and many other spices.
Although Muslim traders first traveled through South East Asia early in the Islamic era, the spread of Islam among the inhabitants of the Indonesian archipelago dates to the 13th century in northern Sumatra.Although it is known that the spread of Islam began in the west of the archipelago, the fragmentary evidence does not suggest a rolling wave of conversion through adjacent areas; rather, it suggests the process was complicated and slow. The spread of Islam was driven by increasing trade links outside of the archipelago; in general, traders and the royalty of major kingdoms were the first to adopt the new religion.
Other Indonesian areas gradually adopted Islam, making it the dominant religion in Java and Sumatra by the end of the 16th century. For the most part, Islam overlaid and mixed with existing cultural and religious influences, which shaped the predominant form of Islam in Indonesia, particularly in Java. Only Bali retained a Hindu majority. In the eastern archipelago, both Christian and Islamic missionaries were active in the 16th and 17th centuries, and, currently, there are large communities of both religions on these islands.
The Sultanate of Mataram was the third Sultanate in Java, after the Sultanate of Demak Bintoro and the Sultanate of Pajang.
According to Javanese records, Kyai Gedhe Pamanahan became the ruler of the Mataram area in the 1570s with the support of the kingdom of Pajang to the east, near the current site of Surakarta (Solo). Pamanahan was often referred to as Kyai Gedhe Mataram after his ascension.
Pamanahan's son, Panembahan Senapati Ingalaga, replaced his father on the throne around 1584. Under Senapati the kingdom grew substantially through regular military campaigns against Mataram's neighbors. Shortly after his accession, for example, he conquered his father's patrons in Pajang.
The reign of Panembahan Seda ing Krapyak (c. 1601–1613), the son of Senapati, was dominated by further warfare, especially against powerful Surabaya, already a major center in East Java. The first contact between Mataram and the Dutch East India Company (VOC) occurred under Krapyak. Dutch activities at the time were limited to trading from limited coastal settlements, so their interactions with the inland Mataram kingdom were limited, although they did form an alliance against Surabaya in 1613. Krapyak died that year.
Krapyak was succeeded by his son, who is known simply as Sultan Agung ("Great Sultan") in Javanese records. Agung was responsible for the great expansion and lasting historical legacy of Mataram due to the extensive military conquests of his long reign from 1613 to 1646.
After years of war Agung finally conquered Surabaya. The city surrounded by land and sea and starved it into submission. With Surabaya brought into the empire, the Mataram kingdom encompassed all of central and eastern Java, and Madura; only in the west did Banten and the Dutch settlement in Batavia remain outside Agung's control. He tried repeatedly in the 1620s and 1630s to drive the Dutch from Batavia, but his armies had met their match, and he was forced to share control over Java.
In 1645 he began building Imogiri, his burial place, about fifteen kilometers south of Yogyakarta. Imogiri remains the resting place of most of the royalty of Yogyakarta and Surakarta to this day. Agung died in the spring of 1646, with his image of royal invincibility shattered by his losses to the Dutch, but he did leave behind an empire that covered most of Java and its neighboring islands.
Upon taking the throne, Agung's son Susuhunan Amangkurat I tried to bring long-term stability to Mataram's realm, murdering local leaders that were insufficiently deferential to him, and closing ports so he alone had control over trade with the Dutch.
By the mid-1670s dissatisfaction with the king fanned into open revolt. Raden Trunajaya, a prince from Madura, lead a revolt fortified by itinerant mercenaries from Makassar that captured the king's court at Mataram in mid-1677. The king escaped to the north coast with his eldest son, the future king Amangkurat II, leaving his younger son Pangeran Puger in Mataram. Apparently more interested in profit and revenge than in running a struggling empire, the rebel Trunajaya looted the court and withdrew to his stronghold in East Java leaving Puger in control of a weak court.
Amangkurat I died just after his expulsion, making Amangkurat II king in 1677. He too was nearly helpless, though, having fled without an army or treasury to build one. In an attempt to regain his kingdom, he made substantial concessions to the Dutch, who then went to war to reinstate him. For the Dutch, a stable Mataram empire that was deeply indebted to them would help ensure continued trade on favorable terms. They were willing to lend their military might to keep the kingdom together. Dutch forces first captured Trunajaya, then forced Puger to recognize the sovereignty of his elder brother Amangkurat II. The kingdom collapsed after a two-year war, in which power plays crippled the Sunan.
In 1524–25, Sunan Gunung Jati from Cirebon, together with the armies of Demak Sultanate, seized the port of Banten from the Sunda kingdom, and established The Sultanate of Banten. This was accompanied by Muslim preachers and the adoption of Islam amongst the local population. At its peak in the first half of the 17th century, the Sultanate lasted from 1526 to 1813 AD. The Sultanate left many archaeological remains and historical records.
| Prehistory | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Early kingdoms | ||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||
| Rise of Muslim states | ||||||||||||||||||||
|

No comments:
Post a Comment